| |
| Exposing the Outlook Password Secrets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Microsoft Outlook is the popular
email client used within the enterprises worldwide. It provides
multiple type of email configuration including Exchange Server,
POP3, IMAP, HTTP etc.
Like many applications, Outlook also stores the account password for
subsequent logins when user selects the 'Remember Password' option
during authentication. The password is stored in the encrypted
format and only corresponding user can decrypt the password.
Different versions of Outlook store the password at separate
locations using distinct encryption methods.
This research article throws
light on uncovering the password stored by different version of
Outlook on different platforms.
|
| |
|
| All versions of Outlook starting
from 2002 to latest version 2010, store the passwords (other than
exchange server) for various email account such as POP3, IMAP, SMTP,
HTTP at following registry location.
|
|
[Windows NT onwards]
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Windows
Messaging Subsystem\Profiles
[Prior to Windows NT]
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows Messaging
Subsystem\Profiles |
|
Latest Outlook 2013 (version 15.0) stores the account configuration along with encrypted password at following location |
|
|
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Office\15.0\Outlook\Profiles\Outlook
|
|
| Outlook stores other information related to configured email account
such as Email Address, User name, Server etc along with password at this
location.
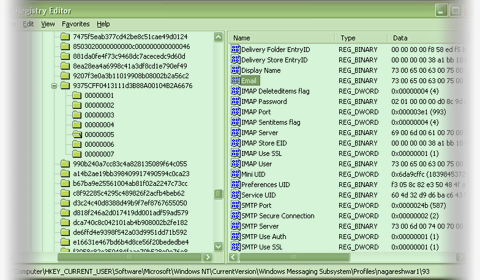
Here is the screenshot of IMAP/SMTP account stored for sample outlook
profile |
|
 |
|
| As shown in the above screenshot different type of accounts
(IMAP/POP3/SMTP/HTTP) uses different registry 'Value Name' to refer to
username, password, server information etc.
Here is the table which summarizes these registry value names for all type of email account
configurations used by Outlook. |
|
| |
Username |
Password |
Email Address |
Server |
Port |
| IMAP |
IMAP User |
IMAP Password |
Email |
IMAP Server |
IMAP Port |
| POP3 |
POP3 User |
POP3 Password |
Email |
POP3 Server |
POP3 Port |
| HTTP |
HTTP User |
HTTP Password |
Email |
HTTP Server URL |
N/A |
| SMTP |
SMTP User |
SMTP Password |
Email |
SMTP Server |
SMTP Port |
|
|
| Except the password, all the other information is stored in clear
text in unicode format. Password is encrypted and has following
structure. |
|
struct OutlookPassword
{
BYTE byteEncType;
BYTE *encPassData;
};
|
|
The byteEncType indicates the encryption mechanism used for storing
the password. Here are possible values for byteEncType
- Windows Protected Storage
- New Windows Cryptography Method
|
|
| Newer versions (2002-2013) of Outlook uses 'Windows Cryptography'
methods to encrypt the password when Outlook is running on Windows NT
platform. For older platforms it uses the 'Windows Protected Storage'
mechanism. The method for decrypting protected storage based passwords
is mentioned the in the
below section on older Outlook version.
Once the password value is read from the registry, decrypting it is
plain task. As mentioned above, make sure that first byte contains value
2 pointing to newer method of encryption. In that case, encPassData
value contains the actual encrypted password data which can be decrypted
using CryptUnprotectData function as shown below |
|
DATA_BLOB DataPassword;
DATA_BLOB DataOutput;
DataPassword.cbData =
DataPassword.pbData = (BYTE *) outlookPassword->encPassData;
if( CryptUnprotectData(&DataPassword, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, &DataOutput) )
{
printf("Found the Outlook Password %S ", DataOutput.pbData);
}
|
|
| The above code snippet takes the encrypted password data and length
to form the DATA_BLOB parameter. Then it is passed on to
CryptUnprotectData function to decrypt the password and the clear text
password is stored in the DataOutput parameter on successful execution. |
| |
| |
|
| Newer Outlook version (2002-2013) uses the 'Credential Store' to
store the 'Exchange Server' passwords. It provides more secure mechanism
for storing and retrieving the password than the older 'Protected
Storage' format. This mechanism is mainly used by Windows to securely
store network login passwords.
Here are the locations of credential files used by 'Credential Store' to
store the encrypted passwords on various platforms. |
|
|
| On Windows XP, the encrypted user credentials are stored in the
hidden file called 'Credentials' inside both APPDATA and LOCALAPPDATA
locations mentioned below. |
|
[APPDATA Location]
C:\Documents and Settings\<username>\Application Data\Microsoft\Credentials\<user sid>\
[LOCALAPPDATA Location]
C:\Documents and Settings\<username>\Local Settings\Application Data\Microsoft
\Credentials\<user sid>\
|
|
|
| Vista onwards, the user credentials are stored in the multiple files
with random name (generated using GUID) inside both APPDATA and
LOCALAPPDATA locations mentioned below. (There will be separate
credential file for each of the network accounts) |
|
[APPDATA Location]
C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Credentials\
[LOCALAPPDATA Location]
C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Credentials\
|
|
|
For further details on decrypting
the exchange server password protected by 'Credential Store' refer
to the 'Recovering Domain Network Password Section' of 'Exposing
Secrets of Network Passwords'
|
| |
|
| Older versions of Outlook (Outlook
Express, 98, 2000 etc) stores the Email configuration information
along with encrypted password at following registry location, |
|
[For Outlook installed in Internet
Mail Only Mode Configuration]
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Office\Outlook\OMI Account
Manager\Accounts
[For Outlook in normal mode]
HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Internet Account Manager\Accounts |
|
| Here Outlook stores all the email
configuration details such as Email Address, User name, Server etc
along with encrypted password. Unlike new Outlook version, older
ones stored password for all type of accounts including 'Exchange
Server' in the 'Windows Protected Storage'.
However the storage format in the registry is similar to new Outlook
versions with the slight change in the registry value names. Here is
the table which summarizes various registry value names for
different type of email account
configurations used by older Outlook versions. |
|
| |
Username |
Password |
Email Address |
Server |
Port |
| IMAP |
IMAP User Name |
IMAP Password2 |
SMTP Email Address |
IMAP Server |
IMAP Port |
| POP3 |
POP3 User Name |
POP3 Password2 |
SMTP Email Address |
POP3 Server |
POP3 Port |
| HTTP |
HTTPMail User Name |
HTTPMail Password2 |
SMTP Email Address |
HTTPMail Server |
N/A |
| SMTP |
SMTP User Name |
SMTP Password2 |
SMTP Email Address |
SMTP Server |
SMTP Port |
| LDAP |
LDAP User Name |
LDAP Password2 |
N/A |
LDAP Server |
N/A |
|
|
| The encrypted password is in below
format (same across all Outlook versions) |
|
|
Since older versions use 'Protected
Storage' method, the byteEncType is always set to 1. Also the encPassData value
actually points to 'password item name' in the Protected storage.
While enumerating protected storage passwords, this item name can be
used to match with corresponding Outlook account password.
The complete program to enumerate and decrypt 'Protected Storage'
passwords is shown in the 'Exposing Secrets of Internet Explorer'
article [Reference 2]. Here additional
check needs to be performed for comparing it with Outlook item names
retrieved from the registry so as to recover only Outlook based
passwords. |
| |
| |
|
|
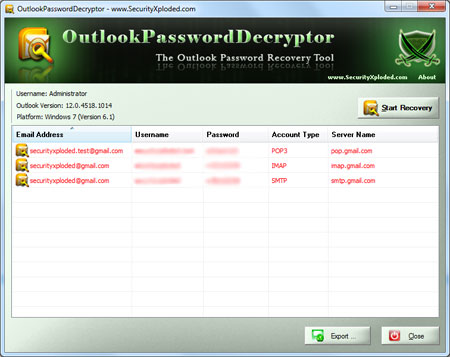
Outlook Password Decryptor is the FREE tool to instantly recover lost password for all
versions of Outlook Application. |
|
 |
|
| Outlook Password Decryptor works on
wide range of platforms starting from Windows 2000 to Windows 10. It
also support password recovery of passwords from all versions
of Outlook . |
|
-
Recovering Domain Network Passwords from 'Credential Store'
-
Decrypting Passwords from 'Protected Storage'
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |